Located between the processor and main memory Secondary Cache L2 3. It separates the computer storage based on hierarchy.
In a fully associative cache every memory location can be cached in any cache line.

. DDR4 faster than ddr3 and uses less power. Theres the L1 data cache but theres also a L1 instruction cache and eg. It is referred to as the level 2 L2 cache.
L1 is the fastest and has the least amount of storage while L2 and L3 become slower but have higher storing capacity. Main memory or primary memory. Cache currently comes in three levels L1 L2 and L3.
There are three distinct level of cache coherence -. Level 3 or L3 Cache Memory. So does the CPU cache size make a difference to performance.
Part of the processor chip Primary Cache L1 2. Generally the L1 cache is the smallest in size and built into the processor chip. Cache hierarchy or multi-level caches refers to a memory architecture that uses a hierarchy of memory stores based on varying access speeds to cache data.
L1 L2 and L3. Memory within the processor housing but not on the processor die 3. SRAM is for older computers.
Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. It works together with the L1 and L2 cache to improve computer performance by preventing bottlenecks due to the fetch and execute cycle taking too long. Highly requested data is cached in high-speed access memory stores allowing swifter access by central processing unit cores.
Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. L1 cache or primary cache is extremely fast but relatively small and is usually embedded in the processor chip as CPU cache. The L3 Cache memory is an enhanced form of memory present on the motherboard of the computer.
The term cache hit means the data or instruction processor need is in cache cache miss in the opposite situation. A Level 3 L3 cache is a specialized cache that that is used by the CPU and is usually built onto the motherboard and in certain special processors within the CPU module itself. The memory hierarchy is again according to the speed and thus the size of the cache.
The Levels of CPU Cache Memory. L1 L2 and L3. This is referred to as the first level cache.
Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2. It is an extra cache built into the motherboard between the processor and main memory to speed up the processing operations. Secondary Cache Secondary cache is placed between the primary cache and the rest of the memory.
A level 2 cache L2 cache is a CPU cache memory that is located outside and separate from the microprocessor chip core although it is found on the same processor chip package. L2 cache or secondary cache is often more capacious than L1. DDR3 faster than ddr2 and uses less power.
Every modern processor comes with a dedicated cache that holds processor instructions and data meant for almost immediate use. Every write operation appears to occur instantaneously. Describe the three levels of cache used by a processor.
There are three different categories graded in levels. L2 cache may be embedded on the CPU or it can be on a separate chip or coprocessor and have a high-speed alternative system bus connecting the. L1 Level 1 cache is the fastest memory that is present in a computer system.
Cache hierarchy is a form and part of memory hierarchy and can be considered a form of tiered. L2 is usually a separate static RAM SRAM chip and it is located between the CPU and DRAM Main memory. Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache.
Intel Core CPUs also have another instruction cache the uOp cache which is depending on your point of view either a parallel L1 instruction cache or a L0 instruction cache. 1 2 3. There is three types of cache.
Memory in the processor package but not on the processor die is called Level 2 cache L2 cache. Magnetic disks or secondary memory. L1 cache is generally built into the processor chip and is the smallest in size ranging from 8KB to 64KB.
DDR2 faster than ddr and uses less power. L1 L2 and L3. All processors see exactly the same sequence of changes of values for each separate.
CPU Cache memory is divided into three levels. There are three general cache levels. In Memory Hierarchy the cost of memory capacity is inversely proportional to speed.
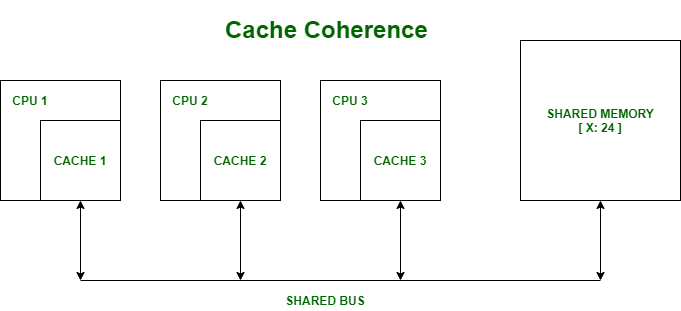
Cache coherence is the discipline that ensures that changes in the values of shared operands are propagated throughout the system in a timely fashion. L1 is usually part of the CPU chip itself and is. The reason it comes in such small amounts is the manufacturing cost and density.
Primary Cache A primary cache is always located on the processor chip. External to the processor Main Memory L3. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache.
Earlier L2 cache designs placed them on the motherboard which made them quite slow. Cache memory within a computer is classified under various types depending upon its physical location within the computer whether they are. In multi-core CPUs a separate L1 cache is available for each core.
Memory on the processor chip is called level 1 cache. Memory on the processor die is called Level 1 cache L1 cache. Cache is graded as Level 1 L1 Level 2 L2 and Level 3 L3.
Some processors use a third cache farther from the processor core but still in the processor package which is called Level 3 cache L3 cache. Optical disks or magnetic types or tertiary Memory. Memory further from the processor core then L2 cache but still within the processor housing.
Examples of L1 cache are. Types of Cache Memory. This cache is small and its access time is comparable to that of processor registers.
Memory on the processor die 2. There are multiple different kinds of cache memory levels as follows Level 1 L1 or Registers It is a type of memory in which data is stored and accepted that are immediately stored in the CPU. First off theres several of them.


0 Comments